What are stroke risk factors and how can they be managed?
This Stroke Awareness Month, Bluecrest is spotlighting the importance of understanding stroke risk factors.
A stroke risk factor refers to any condition, lifestyle choice, or genetic predisposition that increases the likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Strokes occur when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, either by a blockage (ischemic stroke) or a rupture (hemorrhagic stroke).
Risk factors can increase vulnerability to these events.
-
High Blood Pressure: This is the leading cause of strokes. It puts extra strain on blood vessels, making them more likely to burst or become blocked
-
High Cholesterol: Excess cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, restricting blood flow to the brain
-
Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of clot formation
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the likelihood of clots
-
Obesity and Physical Inactivity: Being overweight or inactive can contribute to other risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes
-
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in salt, saturated fats, and cholesterol can increase stroke risk
-
Heart Conditions: Irregular heartbeats (like atrial fibrillation) and other heart diseases can lead to clots that travel to the brain
-
Family History and Age: A family history of strokes or being over 55 years old can increase risk
-
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure and contribute to other risk factors
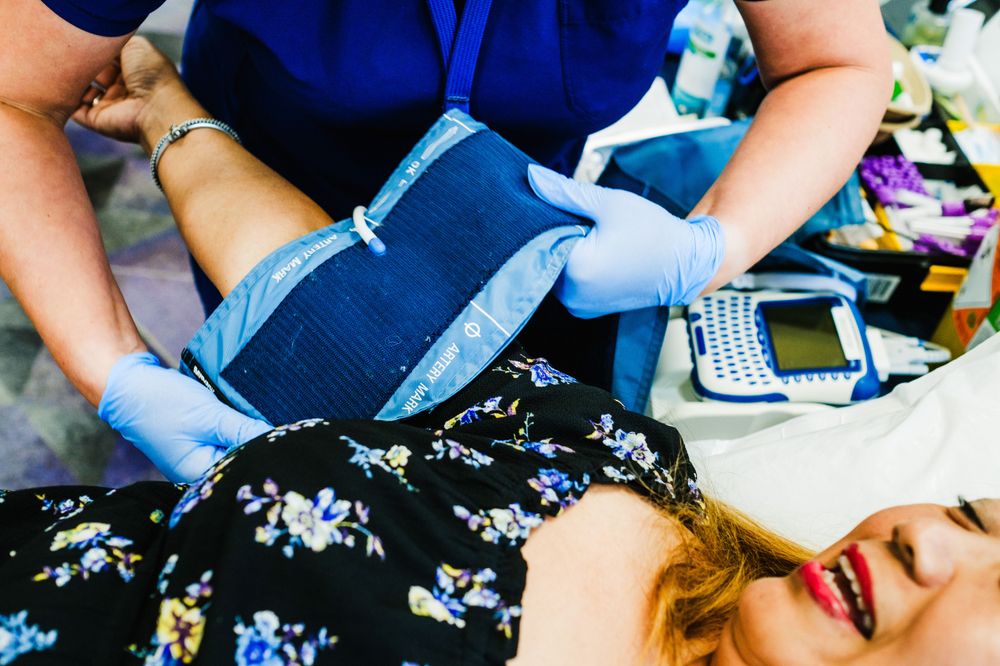
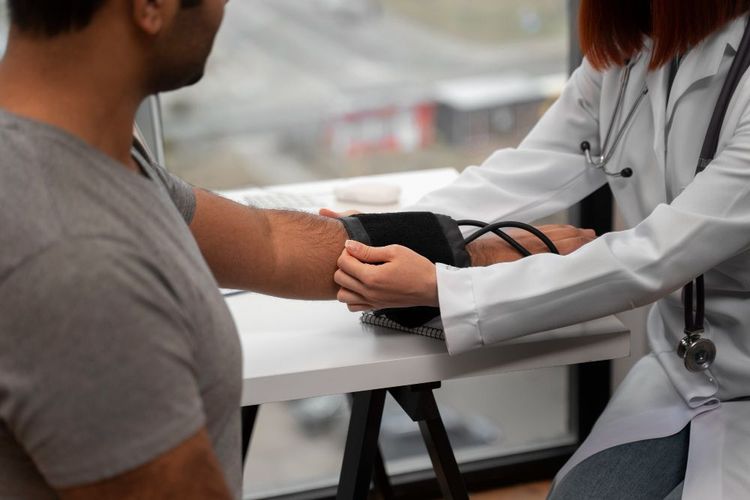
There are multiple ways to manage stroke risk factors. Start by taking control of your health with a Bluecrest health assessment. Because, when you know your health data you can understand it and start impacting change.
A Bluecrest health assessment can help by:
-
Offering you peace of mind through our detailed, clinical-led assessments
-
Identifying key stroke risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol
-
Giving you detailed, easy to understand data in your health report
-
Providing lifestyle recommendations you can implement to reduce risk factors
There are plenty of ways you can change your lifestyle choices, diet and daily habits to limit the likelihood of stroke risk factors, such as:
-
Control Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke. Regular monitoring, reducing salt intake, exercising, and taking prescribed medication can help maintain healthy levels
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases stroke risk. A balanced diet and regular physical activity can help manage weight effectively
-
Exercise Regularly: Engaging in moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking or swimming, for at least 30 minutes a day can improve cardiovascular health
-
Quit Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases stroke risk Quitting smoking significantly lowers the chances of stroke
-
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can raise blood pressure and contribute to stroke risk. Moderation is key
-
Manage Diabetes: Keeping blood sugar levels under control through diet, exercise, and medication reduces stroke risk
-
Monitor Cholesterol Levels: High cholesterol can lead to artery blockages. Eating a heart-healthy diet and taking prescribed medication can help
-
Treat Atrial Fibrillation: This irregular heartbeat condition increases stroke risk. Medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments can help manage it
Need help?
You can reach out to our corporate team on 0808 168 9219